Category: Other
16. Feb 2024
Navigating the Waters: Decoding the Intricacies of Water in NIR Spectroscopy
In today’s fast-paced world of scientific innovation, Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy has established itself as a vital tool across various sectors. This includes pharmaceuticals, food, and agriculture. Renowned for its precision and adaptability, NIR Spectroscopy has revolutionized the way we analyze material composition. Leading this wave of innovation is NIRLAB, equipped

09. Feb 2024
Food Safety: The Future with NIR Technology
In today’s food safety era, Near Infrared (NIR) technology, led by NIRLAB, transforms how we ensure food quality and safety. The WHO stresses safe food’s vital importance, noting global health risks from contamination. NIR technology, under NIRLAB’s guidance, revolutionizes food safety, aligning with the WHO’s concerns about contamination. This calls

07. Feb 2024
Expert Tips for Accurate NIRLAB Spectrometer Analysis
In the dynamic field of substance analysis, NIRLAB distinguishes itself as a tool of remarkable versatility, with applications extending well beyond the scope of narcotics detection. This state-of-the-art instrument has become essential in various sectors, including harm reduction, cannabis analysis, polymer identification, and law enforcement operations. Additionally, to dive deeper
05. Feb 2024
FTIR vs. NIR Spectroscopy: A Comparative Analysis
In the world of spectroscopic analysis, two prominent methods stand out: Near-Infrared (NIR) and Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy. These methods are known for their distinct capabilities and applications. Both techniques are invaluable in the realm of material analysis, providing unique insights into the composition and characteristics of various substances.
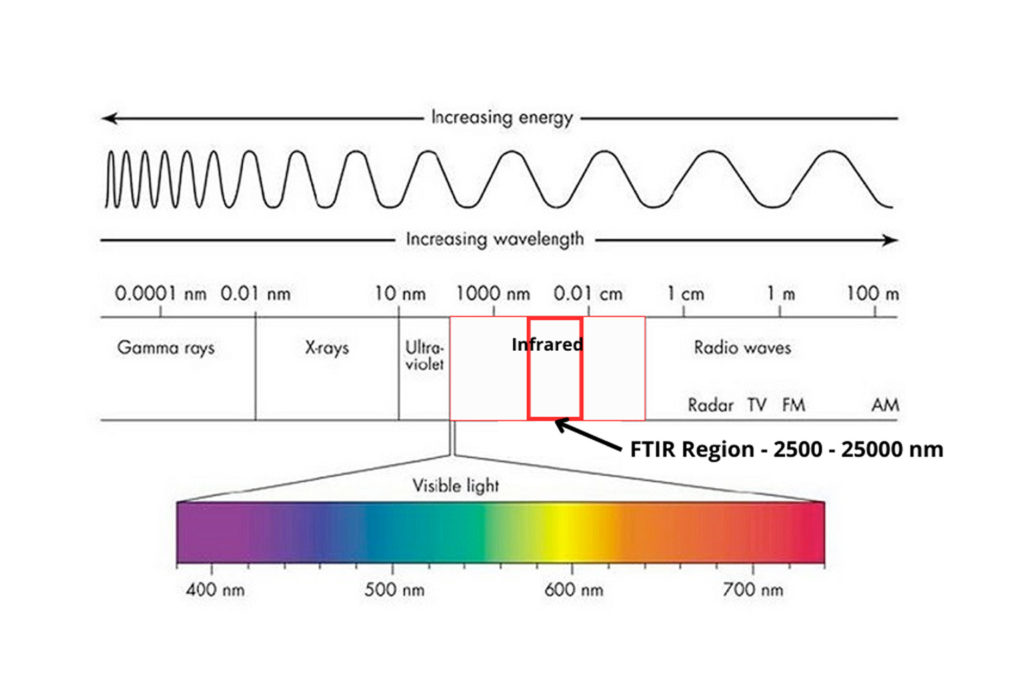
02. Feb 2024
NIRLAB’s Role in Combating Counterfeit Cosmetics to Protect Consumers and Sellers
In an industry as dynamic and rapidly evolving as beauty, the threat of counterfeit cosmetics is a major concern. These imitation products, often skillfully resembling reputable brands, pose significant health risks to consumers and challenge the integrity of authentic businesses. NIRLAB, a leader in Near-Infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, though not currently
